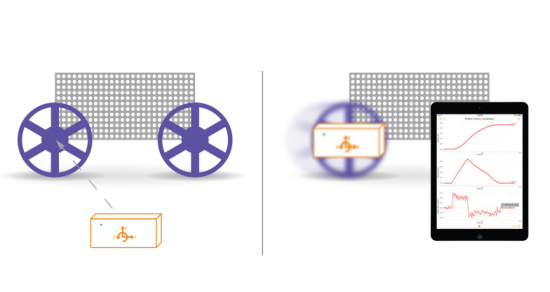
Introduction to Free Falling Objects
Exploration
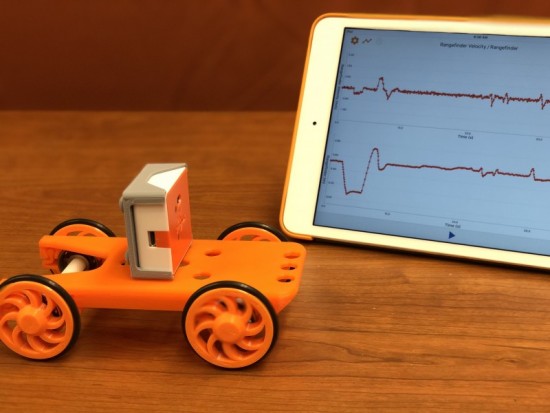
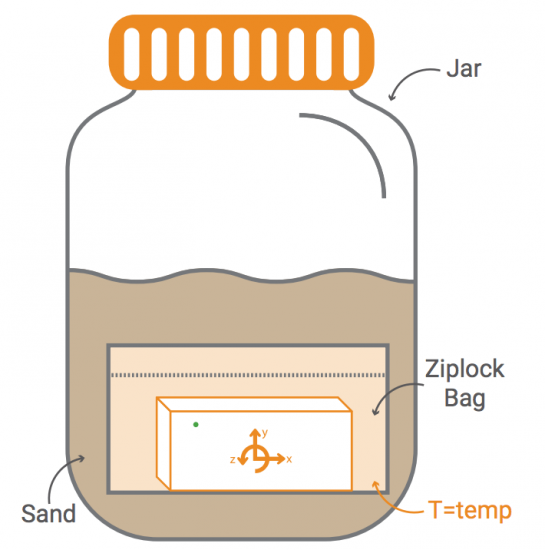
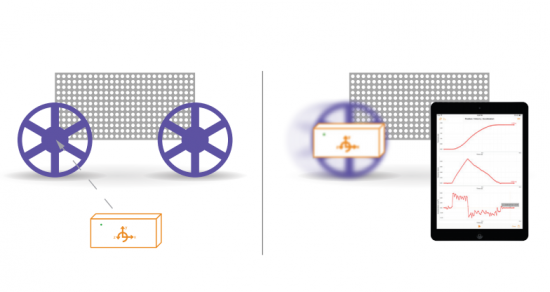
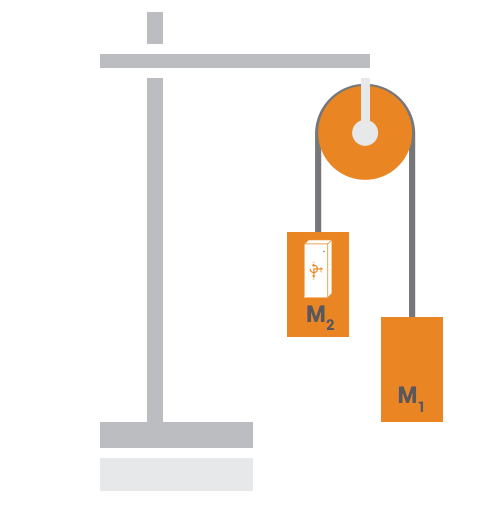
Galileo Galilei is often considered one of the founders of modern science. This is because he investigated questions through experimentation and observations. One of his most famous experiments involved dropping cannonballs of different mass to determine whether they would accelerate to the ground at different rates.