Science Lab: Helmholtz Coils Magnetic Field
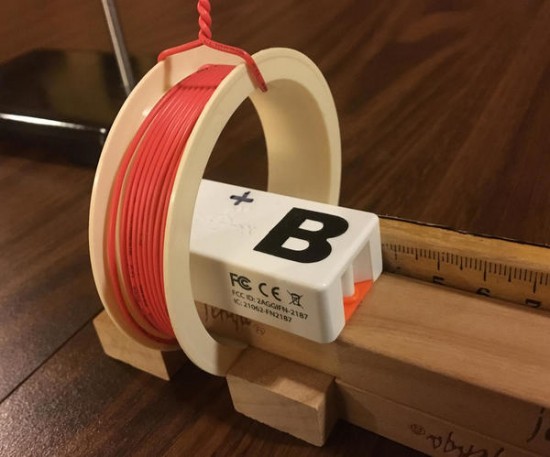
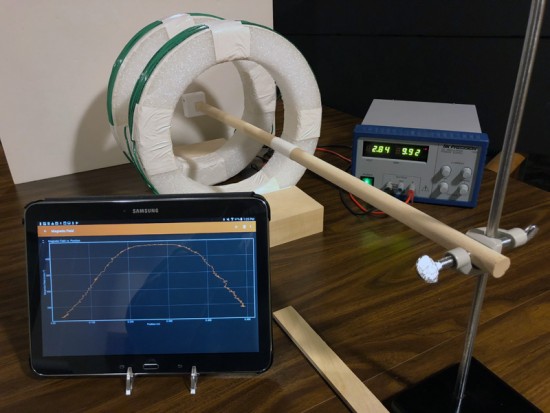
Helmholtz Coils
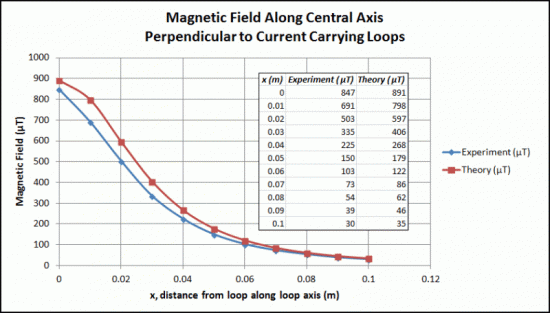
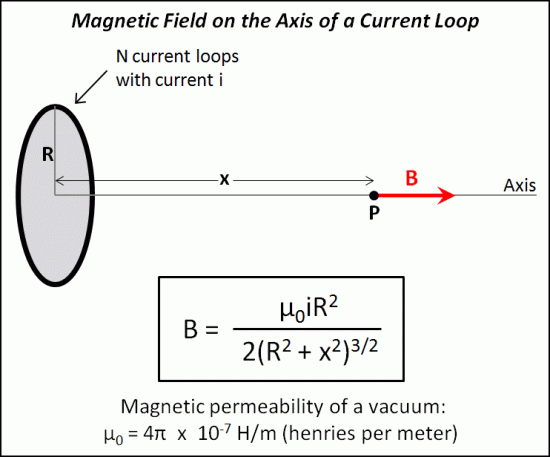
These coils come in pairs with the same number of turns of wire on each of the two coils. In "true Helmholtz" configuration: (1) the coils are wired in series with identical currents in the same direction in each coil, and (2) the coils are placed a distance apart that is equal to the radius of each coil. When in this configuration, they produce a very uniform magnetic field that is directed along their common central axis.