Projectile Motion of an Object
Exploration
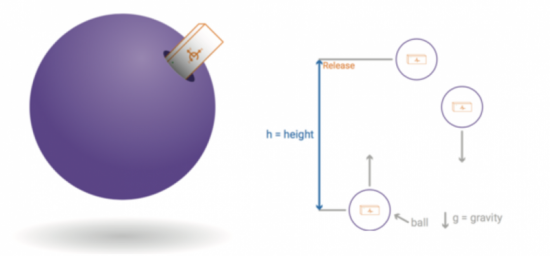
When an object is in free fall, the only force acting on the object is gravity. In general terms, an object moving upward is not considered “falling,” however, if gravity is the only force acting on the object (air resistance being negligible) then the object is in fact in a state of free fall. The projectile motion of an object is the trajectory of an object in free fall near Earth’s surface after being thrown or launched in the air. The curved path of the projectile is under the effect of gravity only after being launched.